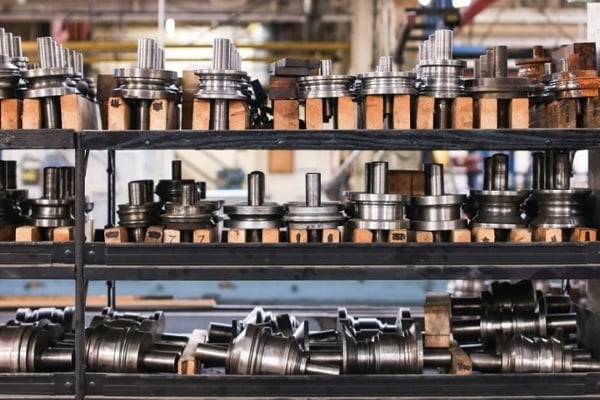
Lean Manufacturing: SMED & Quick Die Changeover

What Is SMED?
SMED stands for Single-Minute Exchange of Dies. Contrary to the name implies, the goal of SMED is not to achieve die exchange in a minute or less, but to reduce die changeover time to under ten minutes.
When setup times are long, manufacturers prefer to run as many pieces as possible. That doesn’t fit with kanban philosophy (smaller, frequent runs), so SMED aims to lower setup times to make small runs a viable option.
There are two primary foundations that help ensure a smooth SMED transition.
SMED Foundations
Implementing SMED should be a relatively painless process. In fact, there are always ways that you can improve SMED implementation.
One of the simplest ways to improve SMED is by passing it through four conceptual stages:
- Ensuring that external setup actions are conducted while the machine is in operation
- Separating internal and external setup actions to ensure that parts function properly and allow for efficient transportation of die and other parts
- Converting internal setup actions to become external
- Improving all other setup actions
Luckily, all these steps can be covered under two primary foundations of SMED:
- Workplace organization
- Visual management
1. Workplace Organization
Everything has a place, and everything in its place. Tools should be available in their correct locations so you’re not scrambling for them during setup.
Think of workplace organization like working in your kitchen: all your kitchen tools have their specific drawer, and if something is out of place it throws off your cooking game.
It’s the same for manufacturers. If everything is taken from and put back in one designated spot, employees don’t have to hunt for tools, which cuts setup time significantly.
2. Visual Management
The purpose of visual management is to quickly identify and correct abnormalities. One familiar visual management practice is placing tools on a shadow board. When the tools are removed, it’s obvious which ones are gone and to which slot they should be returned.
Visual management synthesizes with kanban techniques. Kanban cards are one type of visual management; if the card is moved from its “idle” location, it indicates an action must take place.
Humans are overwhelmingly visual creatures; communication is quickest and easiest when there are obvious visual cues. That’s why important traffic signs are all large, simple, and fun-colored.
Benefits of SMED
- Assists kanban techniques with low inventory levels and high turnover rates
- Lower overall manufacturing cost due to less equipment downtime
- Quicker and better response to customer needs
- Mechanical, procedural, and organizational improvements
- Reduced waste - mostly time and manpower, which translates into money saved
The definition of waste in the context of SMED is “any activity that consumes resources but creates no value for the customer.” So, as we mentioned above, running around looking for unorganized tooling is waste.
SMED is another piece of the lean manufacturing puzzle. To be lean, you have to be highly efficient in your processes, and flexible to changes in the economy and with your clients. Every minute counts. Every bit of time saves results in cost savings for both the manufacturer and the customer.
SMED helps manufacturers shave off those precious minutes to improve lead time, reduce wasted manpower, and offer higher quality service to clients.
SMED Helps You Create Superior Parts
Single-minute exchange of dies is one of the most important aspects of lean manufacturing. Not only can SMED help improve your turnaround time, but it also reduces the amount of time that's wasted while running around and looking for proper tooling.
Ultimately, SMED helps you achieve a truly superior roll formed part that goes above and beyond expectations. To learn even more about what goes into designing a great roll formed part, check out our free e-book below:
Editor's note: This article was originally published in January 2016, and has recently been updated.
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
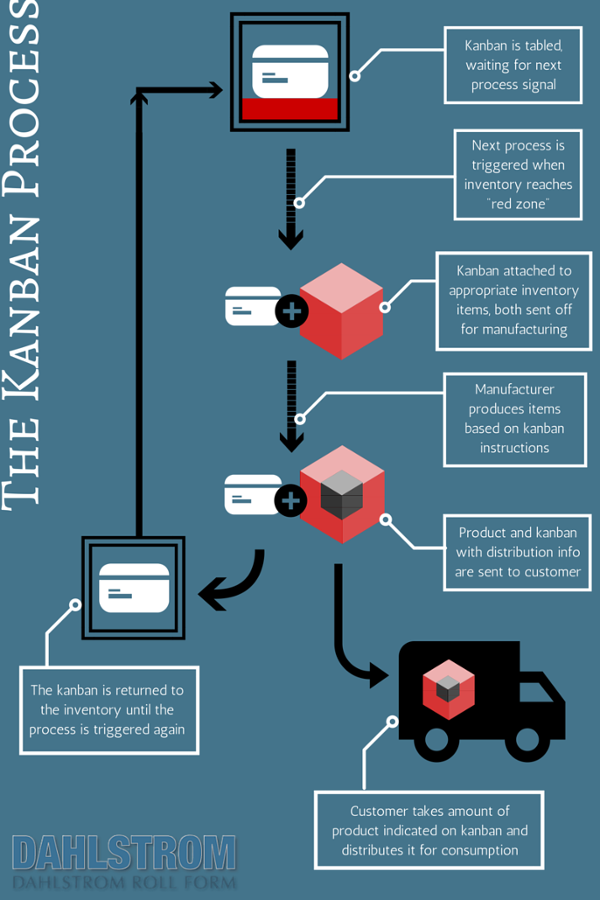
Keep Roll Forming Costs Under Control With Kanban Inventory Management

Why Your Roll Former Needs Better Manufacturing Shipping Solutions





